Overview
Today, a new vulnerability affecting the widely used Samba software was released. Samba is the SMB/CIFS protocol commonly used in *NIX operating systems. CVE-2017-7494 has the potential to impact many systems around the world. This vulnerability could allow a user to upload a shared library to a writeable share on a vulnerable Samba server and result in the server executing the uploaded file. This would allow an attacker to upload an exploit payload to a writeable Samba share, resulting in code execution on any server running an affected version of the Samba package. This currently affects all versions of Samba 3.5.0 (released March of 2010) and later. To emphasize the severity and low complexity: a metasploit one-liner can be used to trigger this vulnerability.
A patch has already been released to address the issue. Additionally, there is a mitigation available within the configuration of Samba itself. Adding the argument "nt pipe support = no" to the global section of the smb.conf file and restarting the service will also mitigate the threat. This threat is only beginning to be recognized by potential attackers with POC code having already been released on the Internet. It is only a matter of time before adversaries begin to use it more widely to compromise additional systems, both externally and internally.
This is likely to affect numerous servers, storage devices such as NAS systems, and anything else running the version of Samba that is vulnerable to this attack. Users are urged to contact their vendor to obtain patched firmware or recommendations for addressing this threat. In the meantime the above workaround may help. In accordance with best practices, it is highly recommended that users do not allow direct SMB, Samba, CIFS, NFS, etc. access from the Internet to systems within their network.
Coverage
Snort Rule: 43002-43004
Open Source Snort Subscriber Rule Set customers can stay up to date by downloading the latest rule pack available for purchase on Snort.org.
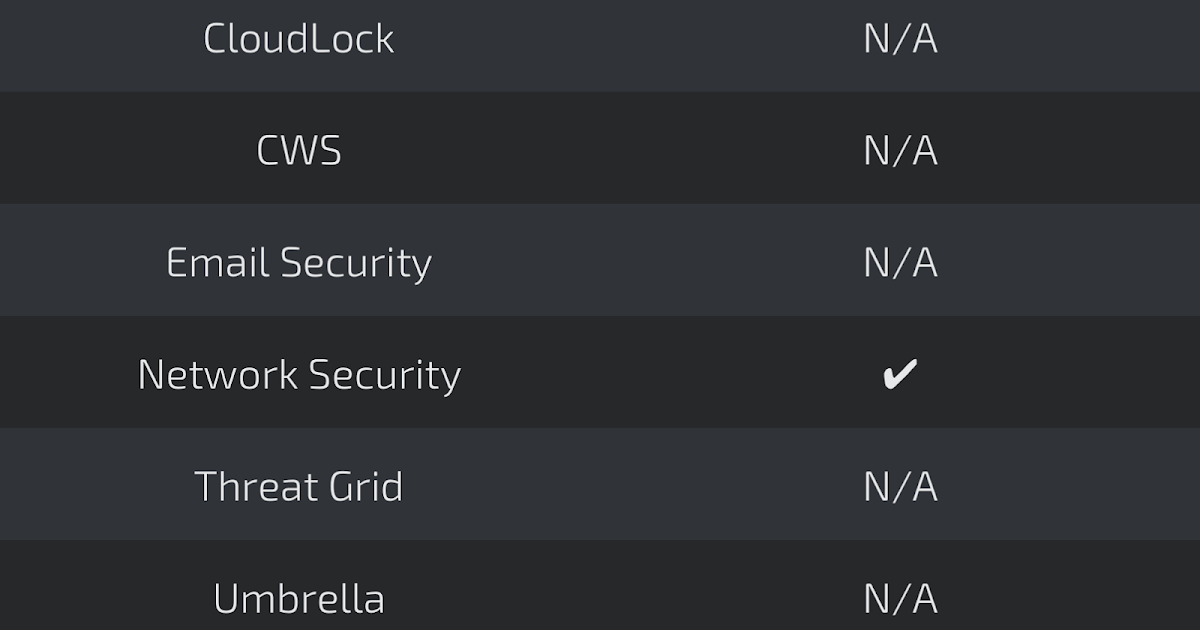
Additional ways our customers can detect and block this threat are listed below.
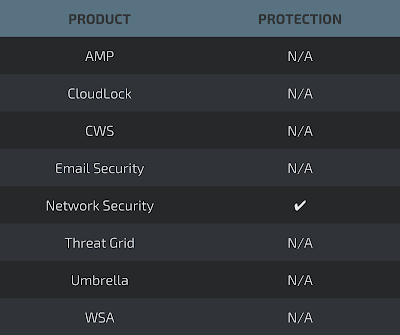
Advanced Malware Protection (AMP) is ideally suited to prevent the execution of the malware used by these threat actors.
CWS or WSA web scanning prevents access to malicious websites and detects malware used in these attacks.
Network Security appliances such as NGFW, NGIPS, and Meraki MX can detect malicious activity associated with this threat.
AMP Threat Grid helps identify malicious binaries and build protection into all Cisco Security products.
Umbrella prevents DNS resolution of the domains associated with malicious activity.
Stealthwatch detects network scanning activity, network propagation, and connections to CnC infrastructures, correlating this activity to alert administrators.