This post is also available in:
Overview
Cybersecurity company ESET disclosed another Ukraine-focused wiper dubbed "CaddyWiper" on March 14. This wiper is relatively smaller than previous wiper attacks we've seen in Ukraine such as "HermeticWiper" and "WhisperGate," with a compiled size of just 9KB.
The wiper discovered has the same compilation timestamp day (March 14) and initial reports suggest that it was deployed via GPO.
Cisco Talos is actively conducting analysis to confirm the details included in these reports.
Analysis
The wiper is relatively small in size and dynamically resolves most of the APIs it uses. Our analysis didn't show any indications of persistency, self-propagation or exploitation code.
Before starting any file destruction, it checks to ensure that the machine is not a domain controller. If the machine is a domain controller, it stops execution.

Pseudo-code: CaddyWiper checking for the Domain Controller role of the machine.
If the system is not a domain controller, the wiper will destroy files on "C:\Users," followed by wiping of all files in the next drive letter until it reaches the "Z" drive. This means that the wiper will also attempt to wipe any network mapped drive attached to the system.
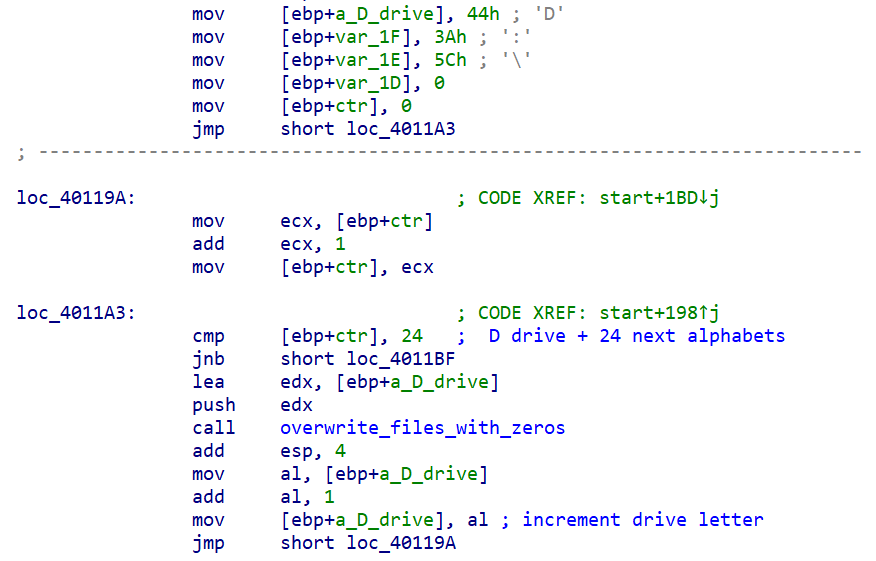
File in drives with letters from D:\ overwritten with zeros.
This ensures that the system will not crash due to the wipe of system files.
File wiping algorithm
The file destruction algorithm is composed of two stages: a first stage to overwrite files and another to destroy the physical disk layout and the partition tables along with it. For the file destruction, it takes ownership of the files by modifying their ACL entries after it has obtained the 'SeTakeOwnershipPrivilege'. A file found will then simply be overwritten with zeros.
A file that is larger than 10,485,760 bytes (0xA00000) in size will simply have the first 10,485,760 bytes overwritten with zeros.
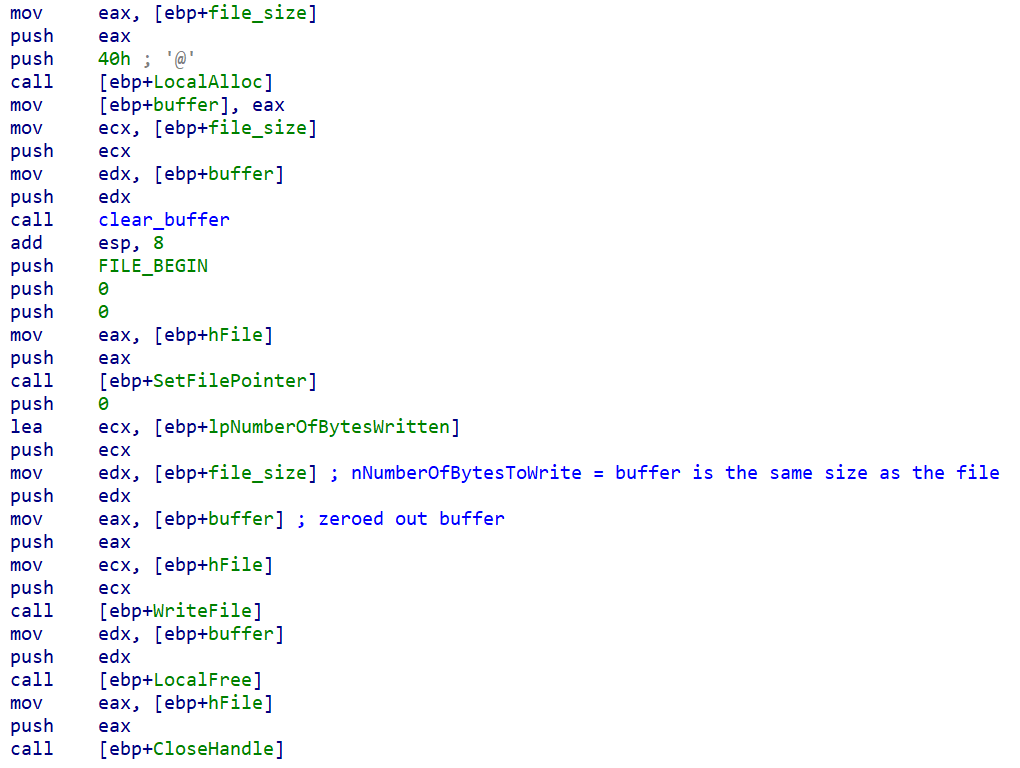
File overwritten with a buffer consisting of zeros.
The wiper will then move on to the next drive on the system beginning with the "D" drive. It will recursively gain rights to files on a drive and overwrite them with zeros. This is done for the next 23 drives alphabetically (through "Z:\").
On the second stage, the wiper attempts to set the drive layout of all the physical drives on the system numbered 9 to 0. This will wipe out all extended information about the physical drive's partitions including MBR, GPT and partition entries.
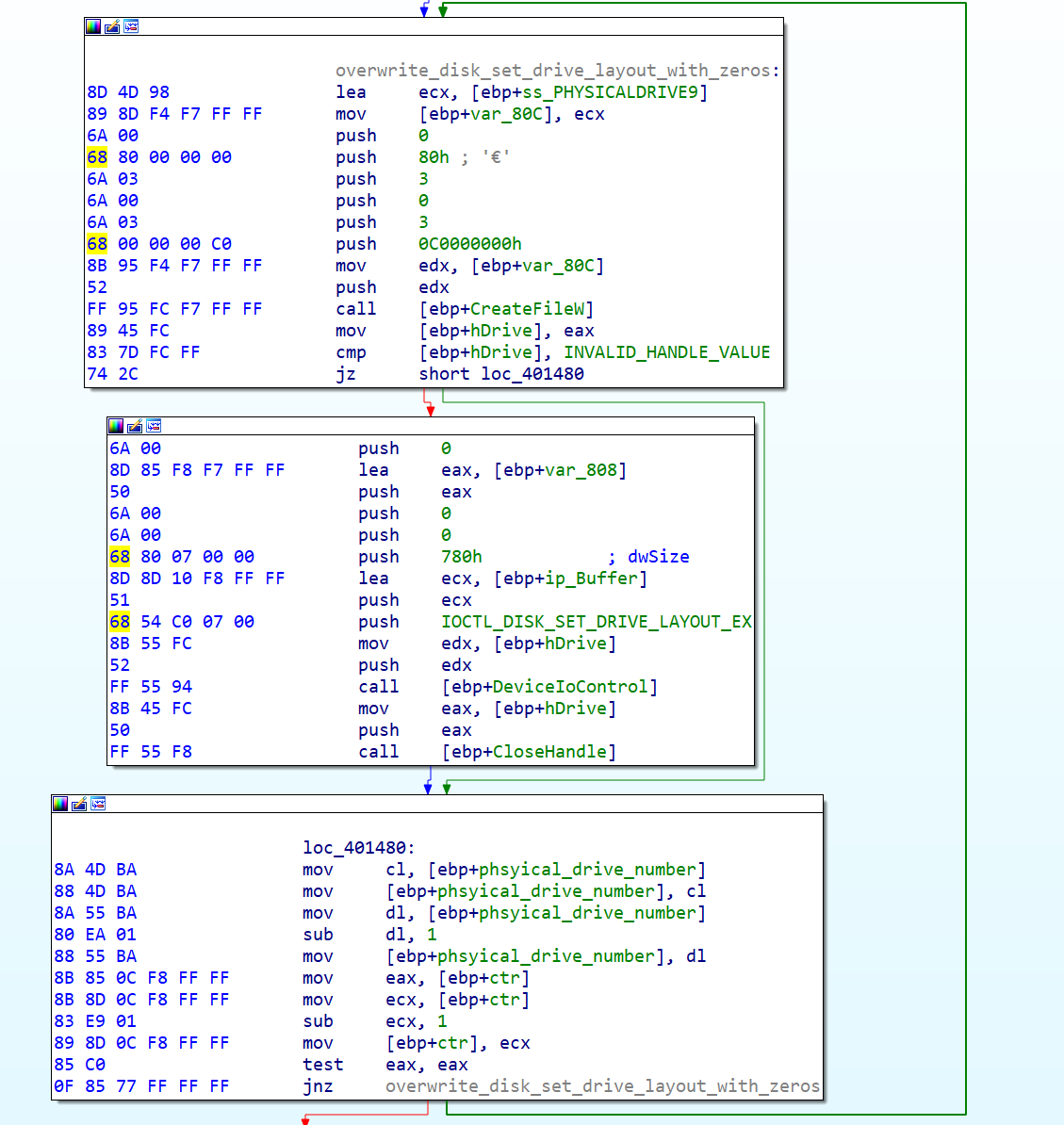
Wiper recursively performing IOCTL_DISK_SET_DRIVE_LAYOUT_EX requests with a zeroed out buffer.
Destroying the start of the files and the partitions tables is a common technique seen on other wipers, and its highly effective in preventing the file recovery.
Coverage
Ways our customers can detect and block this threat are listed below.
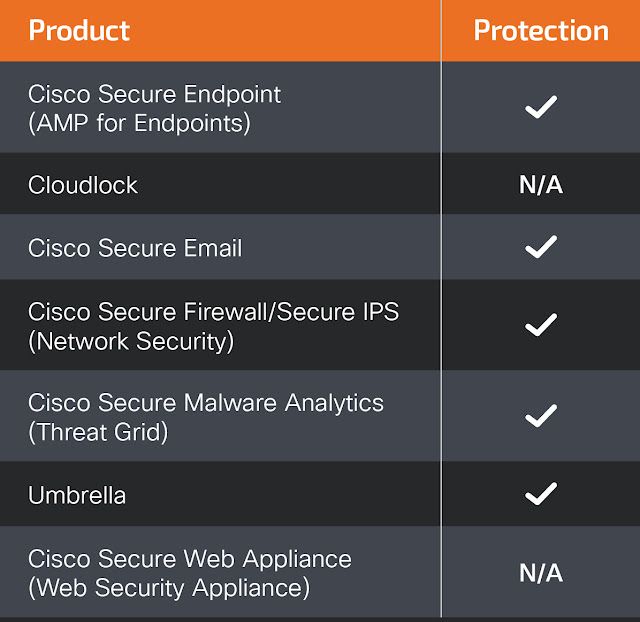
Cisco Secure Endpoint (formerly AMP for Endpoints) is ideally suited to prevent the execution of the malware detailed in this post. Try Secure Endpoint for free here.
Cisco Secure Web Appliance web scanning prevents access to malicious websites and detects malware used in these attacks.
Cisco Secure Email (formerly Cisco Email Security) can block malicious emails sent by threat actors as part of their campaign. You can try Secure Email for free here.
Cisco Secure Firewall (formerly Next-Generation Firewall and Firepower NGFW) appliances such as Firepower Threat Defense (FTD), Firepower Device Manager (FDM), Threat Defense Virtual, Adaptive Security Appliance can detect malicious activity associated with this threat.
Cisco Secure Malware Analytics (formerly Threat Grid) identifies malicious binaries and builds protection into all Cisco Secure products.
Cisco Secure Network/Cloud Analytics (Stealthwatch/Stealthwatch Cloud) analyzes network traffic automatically and alerts users of potentially unwanted activity on every connected device.
For guidance on using Cisco Secure Analytics to respond to this threat, please click here.
Meraki MX appliances can detect malicious activity associated with this threat.
Umbrella, Secure Internet Gateway (SIG), blocks users from connecting to malicious domains, IPs and URLs, whether users are on or off the corporate network. Sign up for a free trial of Umbrella here.
Additional protections with context to your specific environment and threat data are available from the Firewall Management Center.
Cisco Duo provides multi-factor authentication for users to ensure only those authorized are accessing your network.
Open-source Snort Subscriber Rule Set customers can stay up to date by downloading the latest rule pack available for purchase on Snort.org.
Snort SIDs: 59268-59269
The following ClamAV signatures available for protection against this threat:
- Win.Malware.CaddyWiper-9941573-1
IOCs
a294620543334a721a2ae8eaaf9680a0786f4b9a216d75b55cfd28f39e9430ea
1e87e9b5ee7597bdce796490f3ee09211df48ba1d11f6e2f5b255f05cc0ba176
ea6a416b320f32261da8dafcf2faf088924f99a3a84f7b43b964637ea87aef72
f1e8844dbfc812d39f369e7670545a29efef6764d673038b1c3edd11561d6902
