Update 12/14: Cisco Talos has implemented additional blocks in relation to the supply chain attack on SolarWinds® Orion® Platform. The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency has issued Emergency Directive 21-01 due to this campaign. Talos is continuing to investigate this matter. If necessary, we will release additional coverage. Please follow the Talos blog or Talos on Twitter for the latest updates. Additional details are available here, hereand here.Cyber security firm FireEye recently disclosed an incident that was reported to have resulted in the inadvertent disclosure of various internally developed offensive security tools (OSTs) that were used across FireEye red-team engagements.
Some of these tools appear to be based on well-known offensive frameworks like Cobalt Strike. This is even evident in the naming convention used in the coverage designated by FireEye.

The use of Cobalt Strike beacons is popular among red teams and adversaries. In 2020, Cisco Talos released a research paper detailing the large amount of coverage for the Cobalt Strike framework. We have concluded the coverage is still applicable and can reliably detect FireEye red team beacons and other activity.
It has been reported that none of the tools target zero-day vulnerabilities.
FireEye provided a list of CVEs in their blog to allow customers to assess their vulnerability to the tools. Here is the existing coverage for those CVEs:
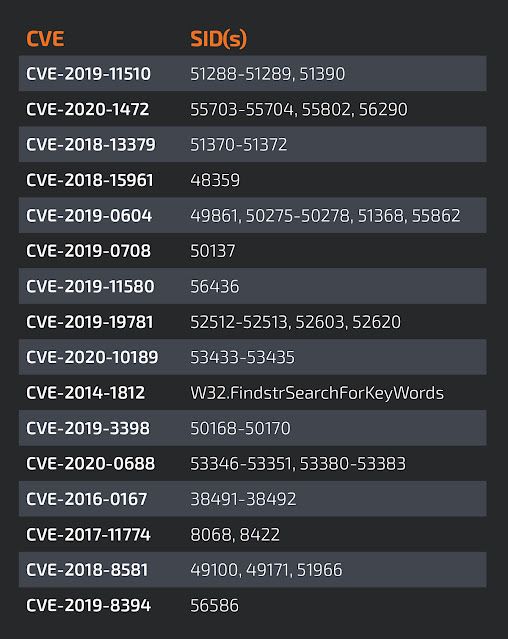
Many of these tools and the vulnerabilities they exploit should be covered by existing defensive products.
It’s currently unknown why a state-sponsored actor would want to target these tools. Typically, these types of actors target high-value data possessed by victims.
As part of this disclosure, FireEye also released a repository of signatures/rules designed to detect the use of these tools across a variety of detection technologies.
Details regarding the initial compromise at FireEye, as well as details around additional data targeted by the attackers have not been released to the public.