By Teoderick Contreras and Jose Hernandez of Splunk, with contributions from the Splunk Threat Research Team.
Cryptodrainer scams have emerged as a significant threat in the cryptocurrency ecosystem, targeting unsuspecting individuals with the promise of easy profits while covertly siphoning their digital assets.
Initially, cryptodrainer scams primarily manifested as fraudulent investment schemes, promising high returns on investments in dubious projects or fake initial coin offerings (ICOs). These scams exploited the speculative nature of cryptocurrency markets, luring investors with the allure of quick riches and revolutionary technology. However, instead of delivering on their promises, scammers absconded with investors' funds.
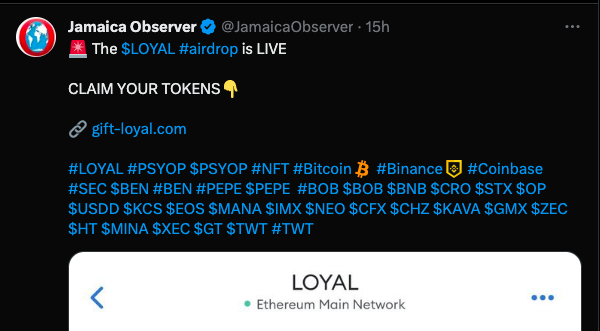
Cryptodrainer phishing scams targeting cryptocurrency holders have become increasingly sophisticated, with scammers employing social engineering techniques to trick users into divulging their private keys or login credentials. These stolen assets were then swiftly drained from victims' wallets, often leaving them with little recourse for recovery.
In recent months, a surge in cryptodrainer phishing attacks has been observed, targeting cryptocurrency holders with sophisticated schemes aimed at tricking them into divulging their valuable credentials. These tactics involve deceptive URLs, carefully crafted to resemble legitimate cryptocurrency platforms, enticing unsuspecting users to input their sensitive login information.
One particularly concerning trend is the emergence of phishing campaigns proliferating across various social media platforms, including X (Twitter). In these instances, compromised accounts, likely hijacked by cybercriminals, are used as unwitting conduits to deliver the malicious URLs to a wider audience. The compromised accounts lend an air of legitimacy to the fraudulent scheme, thereby increasing the likelihood of unsuspecting users falling victim to the scam.
These types of platforms have long been rife for abuse and scams. Cisco Talos has previously highlighted how various aspects of “Web 3” such as the metaverse and smart contracts have been abused to trick users into emptying their cryptocurrency wallets. Malicious Google Forms documents have also been used as an attack vector for these scams.
Anatomy of a crytodrainer attack
Splunk researchers used the Splunk Attack Analyzer to gain insights into the anatomy of this phishing campaign, which we believe follows the same general infection method and attack pattern of cryptodrainer scams.
Below are a few examples of phishing website pages designed to mimic legitimate cryptocurrency platforms, enticing users to disclose their cryptocurrency login credentials.
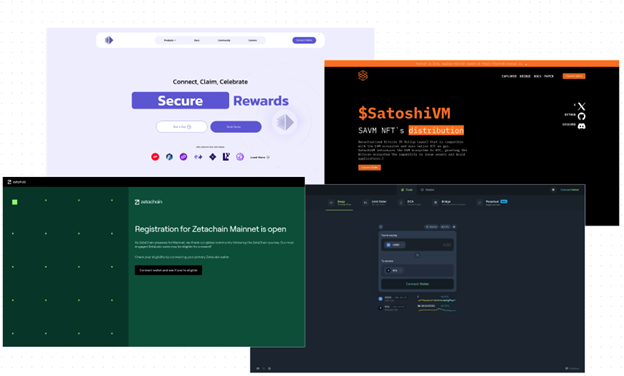
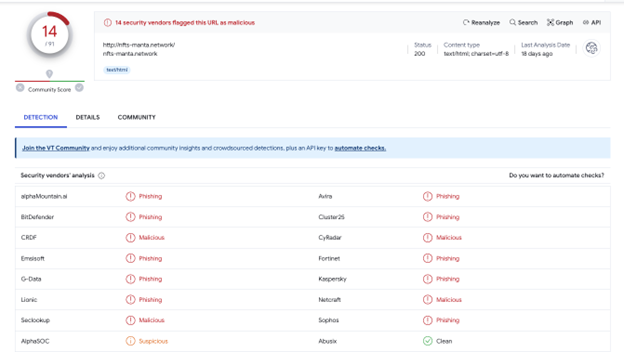
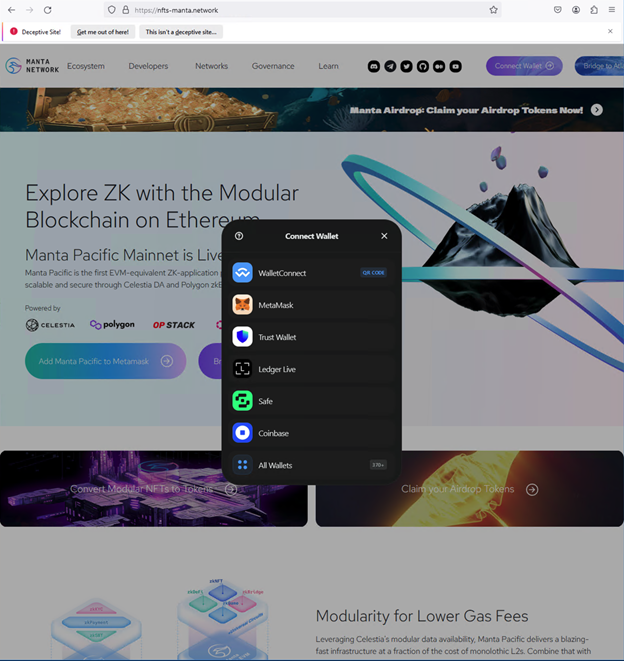
Splunk expanded our repository of potential cryptodrainer phishing URLs using the Attack Analyzer. One such example is hxxp[://]nfts-manta[.]network/, a site identified and flagged as a phishing site by several anti-virus products, according to VirusTotal.
Splunk Attack Analyzer also provides a comprehensive overview, including the landing page screenshot of the phishing site, potential URL link redirections, detections and related artifacts, facilitating further in-depth analysis.
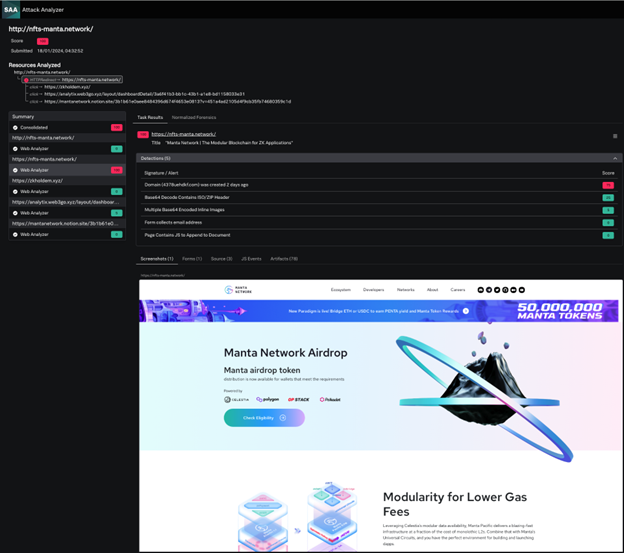
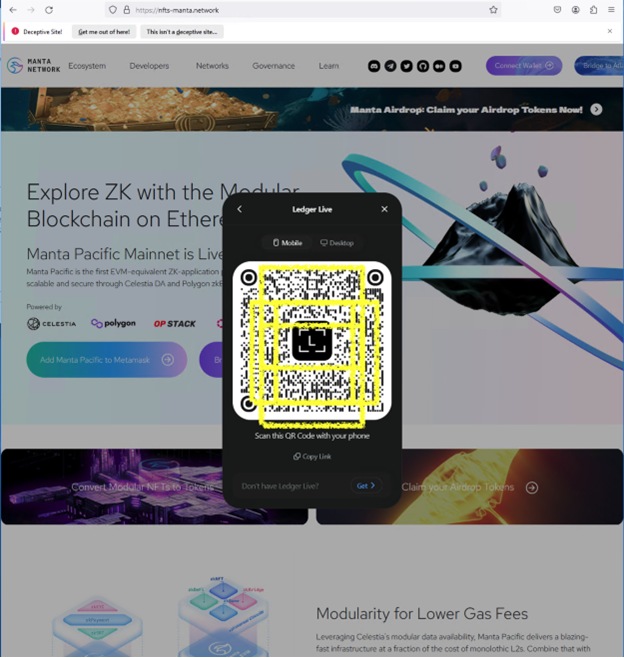
Upon accessing this phishing site, users are prompted to connect their cryptocurrency wallets to purportedly claim tokens. A common method observed for wallet connection involves scanning a QR code using a mobile phone. This QR code may seemingly link to the desired cryptocurrency wallet app, offering the illusion of a seamless login process. In reality, this action grants the phishing site access to the user's login credentials, enabling the unauthorized draining of their cryptocurrency wallet.
Why should you care?
Understanding and staying vigilant against cryptodrainer scams is important for safeguarding your financial well-being and data security.
These scams, often executed through phishing tactics, pose significant risks to individual's finances and personal information if they are invested at all in cryptocurrency.
By remaining informed about the tactics employed by scammers, you can take proactive measures to protect yourself and prevent potential financial losses. Additionally, spreading awareness about these scams helps mitigate their impact by empowering others to recognize and avoid falling victim to fraudulent schemes.
Here are a few tips for spotting possible cryptocurrency scams like the ones outlined above:
- Carefully consider and thoroughly research before registering for, or investing, in any cryptocurrency that promises quick and significant returns. High-reward opportunities often come with high risks, and many such promises may be scams. As always, if it seems too good to be true, it probably is.
- Always verify the legitimacy of the website before providing your personal information or registering your cryptocurrency accounts or wallet. Look for signs of credibility such as secure URLs (https), professional design and positive reviews from trusted sources.
- Ensure that your security products are consistently updated to detect and block known malicious websites that employ these deceptive tactics. Regular updates provide the latest protection against evolving threats and scams in the cryptocurrency space.
By following these guidelines, you can better protect yourself from the risks associated with investing in cryptocurrencies and engaging with online platforms.
Coverage
The following Splunk SOAR playbooks integrate with Splunk Attack Analyzer and other sandbox tools, allowing users and admins to easily triage and identify this type of activity in a given environment.
Playbook | Description |
Accepts URL link, domain or vault_id (hash) to be detonated using Splunk Attacker (SAA) API connector. This playbook produces a normalized output for each user and device. | |
Leverages Splunk technologies to determine if a .eml or .msg file in the vault is malicious, whether or not it contained suspect URLs or Files, and who may have interacted with the IoCs (emails, URLs or files). | |
Automatically dispatches input playbooks with the 'sandbox' tag. This will produce a merge report and indicator tag for each input. |
Below is a list of other IOCs related to cryptodrainer scams.
hxxps://123-bti[.]pages[.]dev/
hxxps://giveaway-omnicat[.]pages[.]dev/
hxxps://visit-ait[.]pages[.]dev/
hxxps://enrol-manta[.]network/
hxxp://nfts-manta[.]network/
hxxp://nftbonus-manta[.]network/
hxxps://sea-manta[.]network/
hxxps://sale-starknet[.]io/
hxxps://gain-manta[.]pages[.]dev/
hxxps://frame-343[.]pages[.]dev/
hxxps://gainsatoshi[.]pages[.]dev/
hxxps://visit-dymension[.]pages[.]dev/
hxxps://manta11[.]pages[.]dev/
hxxps://explore-satoshi[.]pages[.]dev/
hxxps://governance-mantanetwork[.]pages[.]dev/
hxxps://accept-satoshivmio[.]pages[.]dev/
hxxps://preregistration-satoshivmio[.]pages[.]dev/
hxxps://receive-altlayerio[.]pages[.]dev/
hxxps://bonus-8u0[.]pages[.]dev/
hxxps://reveal-manta[.]pages[.]dev/
hxxp://acquire-satoshivm[.]io/
hxxps://farcana123[.]pages[.]dev/
hxxps://enlist-jup[.]app/
hxxps://distributedymension[.]pages[.]dev/
hxxps://visit-lineabuild[.]pages[.]dev/
hxxps://1-67c[.]pages[.]dev/
hxxps://registryzetachain[.]pages[.]dev/
hxxps://gratitude-satoshivm[.]pages[.]dev/
hxxps://whitelist-woo[.]pages[.]dev/
hxxps://join-jupapp[.]pages[.]dev/
hxxps://million-satoshivmio[.]pages[.]dev/
hxxps://achieve-altlayer[.]pages[.]dev/
hxxps://follow-satoshivm[.]io/ 